With an increasing amount of data collected through a multitude of channels, companies need an effective way to centralize and unify this information, while having powerful tools for analyzing and activating data.
What is a CDP?
A CDP is a platform that allows you to collect, centralize, and unify customer data from different sources into a single view of each customer. It can manage both structured and unstructured data and integrate with various marketing and analytics tools to activate this data in real time.
The different categories of CDP
There are two main categories of CDP, each with its own specificities:
- Integrated CDPs: These platforms combine the collection, activation, and consent management of customer data. They offer all-in-one tools for marketers looking for a complete solution.
- Composable CDPs: These CDPs, like DinMo, are modular and flexible. They integrate directly with other technological tools such as data warehouses or campaign management systems. They are ideal for companies that already have a solid technological infrastructure and are looking for a customizable solution.
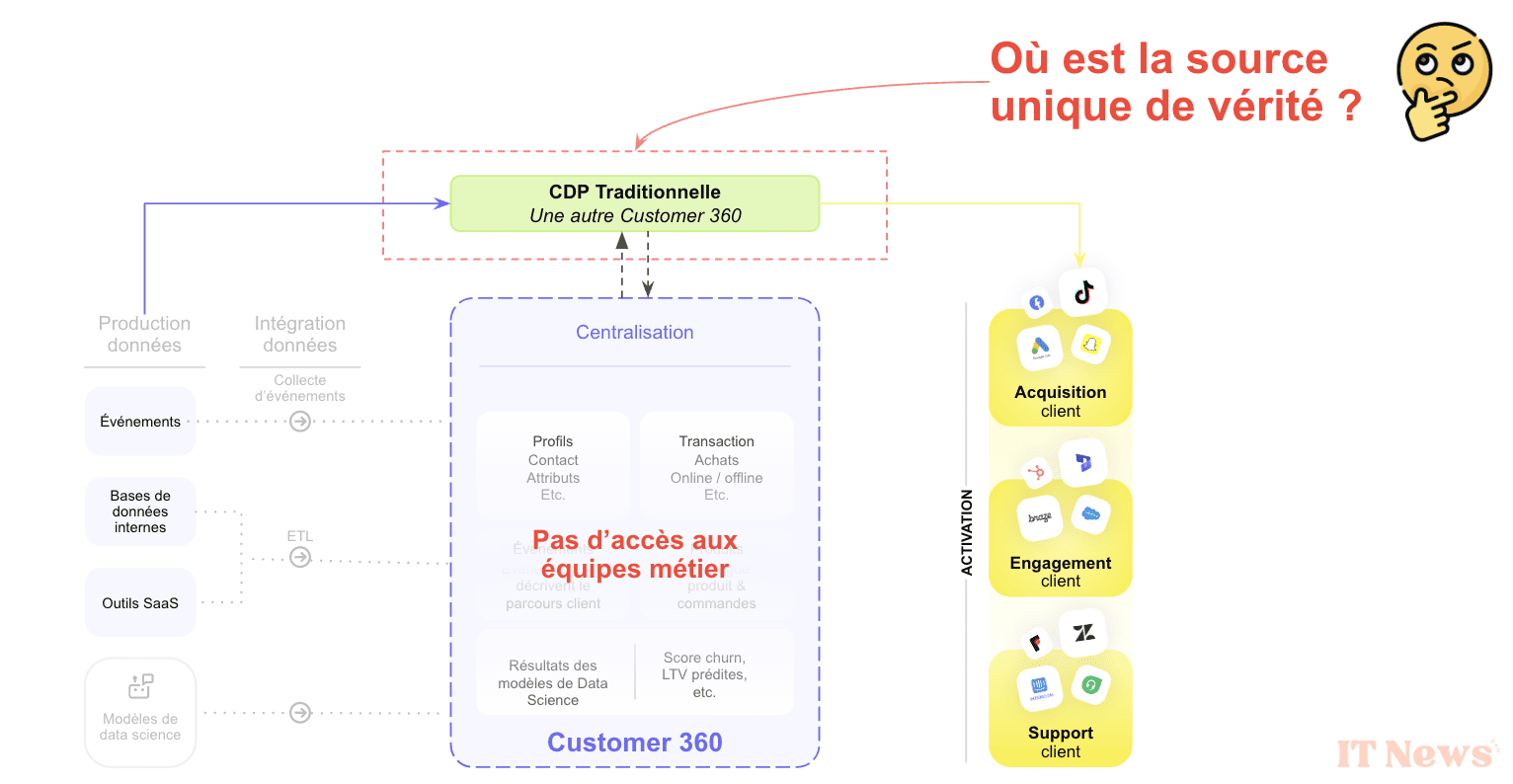
What are CDPs used for in marketing?
In the field of marketing, CDPs are powerful levers allowing companies to better understand and interact with their customers. They enable:
- Centralize customer data: By unifying data from different sources, CDPs provide a complete view of the customer journey, both online and offline.
- Segment audiences: With a CDP, it is possible to segment customers according to precise criteria based on past behaviors, demographic data, or preferences, which allows for the refinement of marketing campaigns.
- Activate data: CDPs can send customer segments to marketing platforms to trigger personalized campaigns based on the specific needs of each segment.
- Improve personalization: Through data centralization and real-time analysis, companies can personalize messages and offers, thus providing a seamless and consistent.
CDP Use Cases
CDPs are used in a multitude of contexts, with varied use cases that illustrate their importance for companies looking to leverage their customer data:
- Improving customer retention: CDPs allow you to track customer behavior across multiple touchpoints. By analyzing these behaviors, it is possible to identify warning signs of disengagement (decrease in purchase frequency, unsubscribe from newsletters, etc.) and respond in real time by launching personalized re-engagement campaigns.
- Cross-selling and up-selling: CDPs provide a 360° view of the customer, including their past purchases and preferences. This knowledge allows businesses to recommend complementary or more expensive products or services.
- Advertising Campaign Optimization: By integrating a CDP with advertising platforms, businesses can create highly specific segments and target their ads more precisely. This helps reduce costs while increasing campaign ROI.
- Customer Journey Personalization: Businesses use CDPs to deliver personalized journeys to their customers.
AI Impact on CDPs
Artificial intelligence is transforming the way CDPs operate and are used. With AI, businesses can now perform even more sophisticated analyses of their data, opening the door to new opportunities:
- Predictive Segmentation: AI helps create segments based on future behaviors, such as the likelihood that a customer will make a purchase or abandon a brand. These segments can be automatically generated and updated based on new behaviors.
- Real-time optimization: With AI, companies can optimize their marketing campaigns in real time, adjusting messages and offers based on customer reactions.
- Process automation: AI can also automate tasks, such as segment creation or product recommendations, freeing marketing teams from repetitive tasks.
Benefits of a CDP
- Advanced personalization: Centralized data enables personalization at scale, improving customer experience and loyalty.
- Improved decisions: Insights from unified data help make fact-based decisions concrete.
- Regulatory Compliance: By centralizing the management of customer consents and preferences, CDPs help companies comply with GDPR requirements.
- Cost Optimization: By making marketing campaigns more precise, CDPs help reduce unnecessary expenses, while maximizing ROI.
With the ability to centralize, analyze, and activate customer data, CDPs have become essential pillars for companies. They help optimize customer interactions and generate considerable ROI.



0 Comments